Sandwich panels are a versatile and popular solution for the construction, refrigeration, and automotive industries due to their excellent insulation properties, durability, and ease of installation. The production of sandwich panels is highly dependent on advanced machinery and technology that ensure high-quality output with consistent performance. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the technology behind sandwich panel production lines, the various processes involved, and the machinery used to create these efficient and reliable panels.
Types of Sandwich Panels
There are several types of sandwich panels available in the market, each suited for specific applications:
- Polyurethane (PU) Sandwich Panels: Known for their high thermal resistance and excellent insulation properties, these panels are commonly used in cold storage facilities and temperature-sensitive environments.
- Polystyrene (EPS) Sandwich Panels: These panels are economical and offer a balance of thermal insulation and strength, making them ideal for standard construction projects.
- Mineral Wool Sandwich Panels: Known for their fire resistance and soundproofing qualities, these panels are ideal for applications requiring high fire safety standards.
- Rock Wool Sandwich Panels: Similar to mineral wool but with even better fire resistance, these panels are used in environments where fire protection is critical.
Key Processes in Sandwich Panel Production Line
A sandwich panel production line involves several processes, from raw material handling to the final inspection and packaging. Below, we outline each step in the production process.
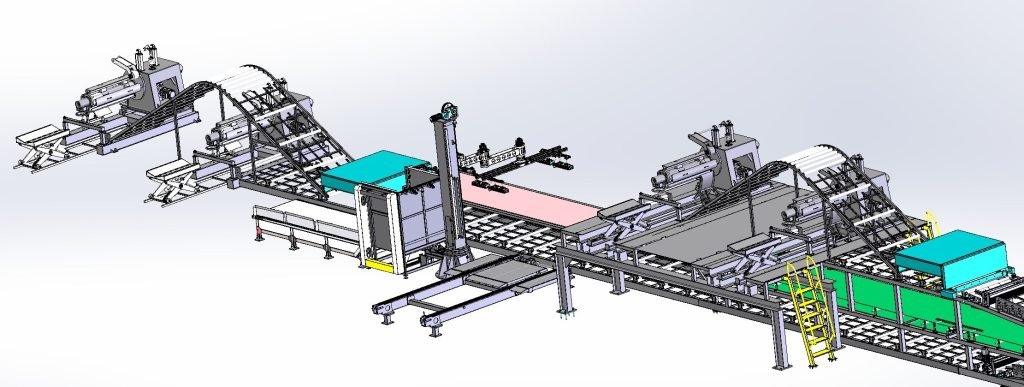
1. Raw Material Feeding
The production line begins with the feeding of raw materials. The outer skins, typically in coil form (steel or aluminum), are fed into the production line. These coils are unwound and prepared for further processing. Similarly, the core material, whether EPS, PU, or mineral wool, is prepped for insertion between the skins.
2. Surface Pre-treatment
Before bonding the outer skins to the core, a surface pre-treatment is performed to ensure optimal adhesion. This includes cleaning the surfaces to remove oils, dust, or any other contaminants that may interfere with the bonding process. Additionally, coatings or primers are applied to enhance the durability and adhesion of the skins.
| Pre-treatment Step | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning | Removal of oils and debris from the skins. | Ensures strong adhesion to core material. |
| Priming | Applying a bonding agent to the skins. | Improves adhesion and corrosion resistance. |
| Coating | Protective coatings to enhance durability. | Prevents rust and prolongs panel lifespan. |
3. Core Material Preparation
The core material plays a critical role in the sandwich panel’s performance. Depending on the type of sandwich panel being produced, the core material is either cut into sheets or injected (in the case of PU) into the space between the two skins. The core material is typically lightweight and provides thermal insulation, while also contributing to the overall structural strength of the panel.
- EPS (Expanded Polystyrene): Typically, the core material is cut into sheets that are then placed between the skins.
- PU (Polyurethane): The core material is injected as a liquid foam that expands and hardens between the skins, providing better insulation.
- Mineral Wool: Used for its fire resistance, this material is pre-formed into slabs that are cut to size.
4. Lamination and Pressing
Lamination is the process where the outer skins are bonded to the core material under heat and pressure. This ensures a strong bond that gives the sandwich panels their strength and stability. The lamination process is crucial for the final quality of the sandwich panels and typically involves either roller lamination or hot-press lamination.
| Lamination Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Roller Lamination | The skins are pressed onto the core material using rollers. | Ensures uniform adhesion and alignment. |
| Hot-Press Lamination | The panels are pressed under heat, curing adhesives and bonding the layers. | Increases bond strength and panel durability. |
5. Cutting and Shaping
After the panels have been laminated, they are cut to the desired size using precision cutting tools. Automated cutting machines are employed to ensure uniformity across all panels. This step is essential for creating panels that are ready for installation with minimal waste. Cutting can be done vertically or diagonally, depending on the design requirements.
6. Quality Control and Inspection
Quality control is an essential aspect of the sandwich panel production process. Once the panels are cut, they undergo various inspections to ensure they meet the required specifications. These include thermal insulation tests, mechanical strength assessments, fire resistance evaluations, and visual inspections to detect any defects in the finished product.
| Test Type | Purpose | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Ensures panels meet insulation standards. | Conduct heat flow tests. |
| Strength Testing | Verifies structural integrity. | Perform mechanical stress tests. |
| Fire Resistance | Confirms fireproof capabilities. | Test panels in a fire exposure environment. |
7. Packaging and Shipping
After passing quality control, the sandwich panels are packaged for shipment. Proper packaging protects the panels from damage during transportation. The packaging may include corner protectors, plastic wrapping, and stacking methods that ensure the panels remain intact during delivery.
Advantages of Sandwich Panel Production Line Technology
Sandwich panel production lines have undergone significant advancements, offering several benefits that have made them increasingly popular:
- Efficiency: The use of automated machinery ensures high production rates, reducing the need for manual labor and speeding up the manufacturing process.
- Customizability: Sandwich panel production lines can be adjusted to create panels of different sizes, thicknesses, and material compositions to suit various applications.
- Consistency and Quality: Automated processes ensure that each panel meets stringent quality standards, leading to consistent results and minimal defects.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The high throughput and reduced waste in the production process make sandwich panels an affordable solution for large-scale projects.
Conclusion
The sandwich panel production line is a critical component of modern manufacturing, offering a range of benefits from high efficiency to customizable solutions. As demand for energy-efficient and durable building materials increases, the role of advanced production technology in producing high-quality sandwich panels becomes ever more important.
If you are in need of high-quality sandwich panels or interested in purchasing a production line for your business, look no further! At [Your Company Name], we specialize in designing and manufacturing top-tier sandwich panel production lines tailored to your needs. For more information or to request a quote, feel free to contact us.



